From Wallets to Blockchains: Unraveling the Mechanics of Cryptocurrency

Welcome to the fascinating world of cryptocurrency, where digital innovation and decentralized technologies converge to redefine the way we think about money. In this blog post, we’ll embark on a journey to unravel the intricate mechanics of cryptocurrency, focusing on key components such as wallets and blockchains.
Understanding Cryptocurrency:
What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency that employs cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology.
The Role of Blockchain:
At the heart of cryptocurrency lies the blockchain, a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions and a reference to the previous block, creating a secure and transparent system.
Exploring Cryptocurrency Wallets:
Types of Cryptocurrency Wallets:
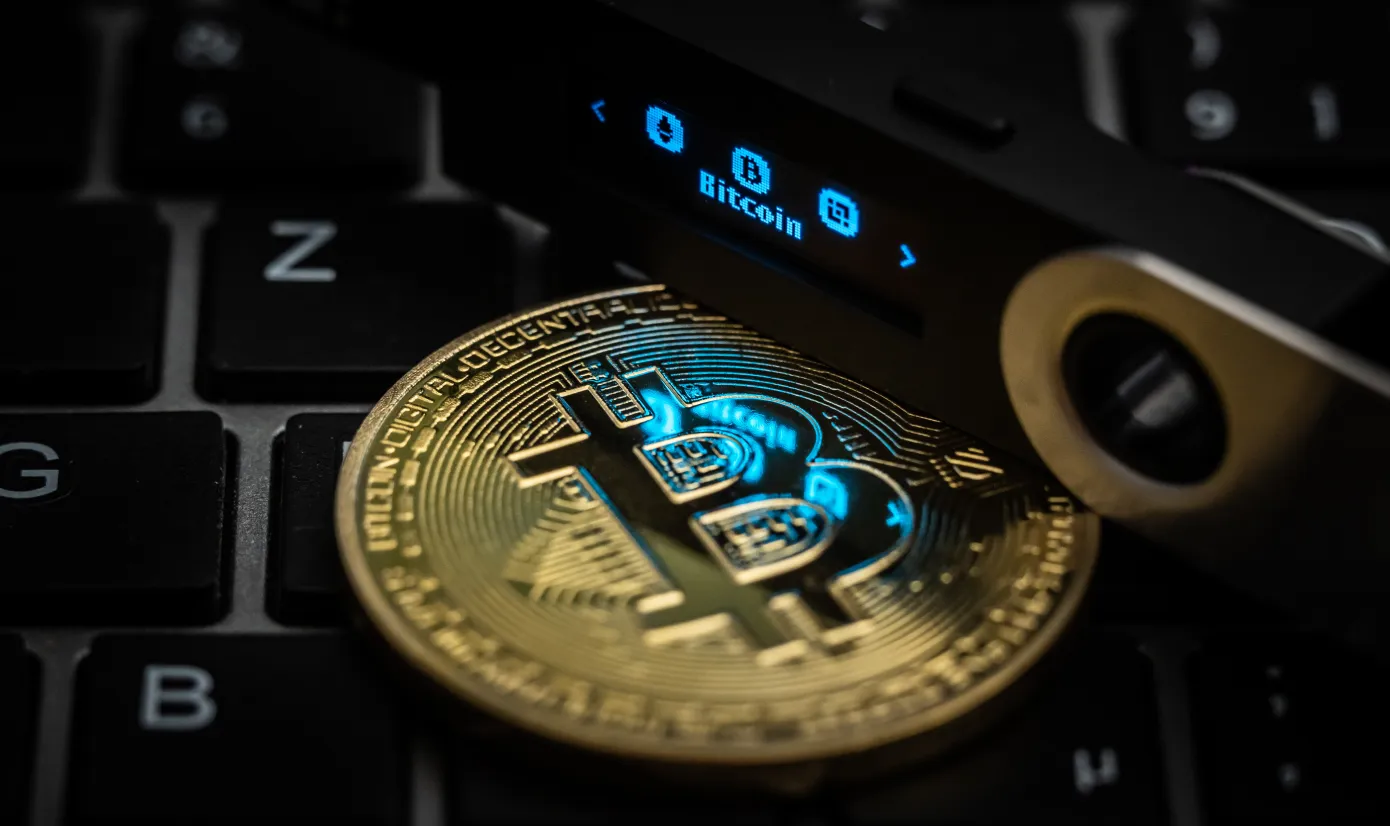
Hardware Wallets: Physical devices that store cryptocurrency offline, providing enhanced security.
Software Wallets: Applications or programs that allow users to store and manage their cryptocurrency on electronic devices.
Paper Wallets: Physical documents containing public and private keys for cryptocurrency storage.
How Wallets Work:
Cryptocurrency wallets store private keys, enabling users to access their funds. When a user initiates a transaction, the wallet signs the transaction with the private key, ensuring the security and authenticity of the transfer.
The Transaction Process:
Initiation: A user decides to send cryptocurrency to another party.
Verification: The transaction is verified by nodes on the blockchain network through a consensus mechanism.
Inclusion in a Block: Once verified, the transaction is added to a block on the blockchain.
Block Confirmation: The block is confirmed through a process such as mining, making the transaction irreversible.
Security Measures:
Cryptography:
Cryptography plays a crucial role in securing transactions and wallets. Public and private key pairs ensure that only the rightful owner can access and control their cryptocurrency.
Decentralization:
The decentralized nature of blockchain technology eliminates the need for a central authority, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation.
The Future of Cryptocurrency:
As we delve deeper into the mechanics of cryptocurrency, it’s essential to consider the future trends that will shape this dynamic landscape.
- Integration of Smart Contracts:
Blockchain technology facilitates the execution of smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This innovation not only automates processes but also enhances the efficiency and transparency of transactions. - Scalability Solutions:
The cryptocurrency community is actively addressing scalability issues to enhance transaction speed and reduce fees. Solutions like Layer 2 scaling and advancements in blockchain consensus mechanisms aim to make cryptocurrencies more practical for everyday transactions. - Interoperability Among Blockchains:
Efforts are underway to establish seamless interoperability among different blockchains. This interoperability will enable the transfer of assets and data across disparate blockchain networks, fostering a more interconnected and collaborative ecosystem.
Overcoming Challenges:
While the potential for growth and innovation in the cryptocurrency space is immense, challenges persist. Security concerns, regulatory uncertainties, and environmental impact are among the issues that the community continues to address.
- Enhancing Security Measures:
Continuous advancements in cryptographic techniques and security protocols are crucial for safeguarding users and their assets. Hardware wallet improvements and biometric authentication are some of the avenues being explored. - Regulatory Clarity:
As governments grapple with the regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies, achieving clarity is essential. Defined regulations can provide a stable environment for innovation and foster broader adoption. - Sustainability Initiatives:
Acknowledging the environmental impact of cryptocurrency mining, the industry is actively exploring sustainable alternatives and transitioning towards more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms.
Conclusion:
In unraveling the mechanics of cryptocurrency, we witness a dynamic ecosystem that goes beyond financial transactions. As technology evolves, so too does the potential for innovation and positive change. Cryptocurrencies are not just currencies; they represent a paradigm shift in how we conceptualize and interact with value.
So, whether you’re an investor, developer, or simply curious about the future of finance, staying informed about the mechanics, trends, and challenges of cryptocurrency positions you at the forefront of this transformative journey. As we navigate this ever-changing landscape together, the future promises exciting developments that will shape the way we perceive and utilize digital assets. Stay tuned for more insights, and happy exploring in the world of cryptocurrency!